LLooM Workbench
The LLooM Workbench is a higher-level API for computational notebooks that surfaces interactive notebook widgets to inspect data by induced concepts. It is defined as the workbench module within the text_lloom Python package and consists of the lloom class.
import text_lloom.workbench as wblloom
lloom(df, text_col, id_col=None, distill_model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", embed_model_name="text-embedding-3-large", synth_model_name="gpt-4-turbo", score_model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", rate_limits={})
A lloom instance manages a working session with a provided dataset. It allows the user to load their dataset and perform rounds of concept induction, concept scoring, and visualization.
Parameters:
df(pd.DataFrame): Text dataset that will be analyzed with LLooM. This dataframe must include a column that contains the input text documents. LLooM expects a dataframe where each row represents a distinct document (or unit of analysis). This is the primary text that will be analyzed with LLooM. The dataframe may also have other columns with additional metadata, which can be used for analysis with LLooM visualizations.text_col(str): Name of the primary text column in the provideddf.id_col(str, optional, default: None): Name of a column with unique IDs for each row. If not provided, the system will assign an ID to each row.distill_model_name(str, optional, default: "gpt-3.5-turbo"): Name of the OpenAI model to use for the Distill operators (filter and summarize).embed_model_name(str, optional, default: "text-embedding-3-large"): Name of the OpenAI embedding model to use for the Cluster operator.synth_model_name(str, optional, default: "gpt-4-turbo"): Name of the OpenAI model to use for the Synthesize operator.score_model_name(str, optional, default: "gpt-3.5-turbo"): Name of the OpenAI model to use for the Score operator.rate_limits(Dict, optional, default: {}): An optional dictionary specifying a mapping from an OpenAI model to its associated rate-limit parameters, a tuple of the form (n_requests, wait_time_secs), where n_requests indicates the number of requests allowed in one batch and wait_time_secs indicates the length of time (in seconds) to wait between batches. Example:{ "gpt-4-turbo": (40, 10) }. If not specified, defaults to the values defined asRATE_LIMITSinllm.py.
Example:
# Creating a LLooM instance
l = wb.lloom(
df=df,
text_col="your_doc_text_col",
id_col="your_doc_id_col", # Optional
)gen
gen(seed=None, params=None, n_synth=1, auto_review=True)
Runs concept generation, which includes the Distill-Cluster-Synthesize operator pipeline.
Parameters:
seed(str, optional, default: None): The optional seed term can steer concept induction towards more specific areas of interest (e.g., social issues" for political discussion or "evaluation methods" for academic papers).params(Dict, optional, default: None): The specific parameters to use within the Distill, Cluster, and Synthesize operators. By default, the system auto-suggests parameters based on the length and number of documents. If specified, the parameters should include the following:py{ "filter_n_quotes": filter_n_quotes, # Number of quotes per document "summ_n_bullets": summ_n_bullets, # Number of bullet points per document "synth_n_concepts": synth_n_concepts, # Number of concepts per cluster/batch }n_synth(int, optional, default: 1): The number of times to run the Synthesize operator.auto_review(bool, optional, default: True): Whether to run a step after the Synthesize operator for the system to review the set of concepts to remove low-quality concepts and merge overlapping concepts.
Examples:
# Default version (no seed)
await l.gen()
# Or: Seed version
await l.gen(
seed="your_optional_seed_term",
)gen_auto
gen_auto(max_concepts=8, seed=None, params=None, n_synth=1)
Runs concept generation, selection, and scoring as a single automated step. In gen_auto, the system makes a call to the LLM to automatically select which concepts to score. By contrast, gen only generates the concepts and allows the user to run the select function to review and select concepts, followed by the score function to perform that scoring. Returns a dataframe with the score results.
Parameters:
max_concepts(int, optional, default: 8): The maximum number of concepts for the system to select out of the set of generated concepts. All of these concepts will be scored. After concept generation, the user is prompted to confirm the set of concepts before scoring proceeds, so there is still an opportunity to review the automatic selection.seed(str, optional, default: None): (Same asgen) The optional seed term can steer concept induction towards more specific areas of interest (e.g., social issues" for political discussion or "evaluation methods" for academic papers).params(Dict, optional, default: None): (Same asgen) The specific parameters to use within the Distill, Cluster, and Synthesize operators. Refer togenfor details.n_synth(int, optional, default: 1): (Same asgen) The number of times to run the Synthesize operator.
Example:
score_df = await l.gen_auto(
max_concepts=5,
seed="your_optional_seed_term",
)select
select()
Allows the user to review and select concepts for scoring. Displays an interactive widget in the notebook.
Example:
l.select()In the output, each box contains the concept name, concept inclusion criteria, and representative example(s). 
select_auto
select_auto(max_concepts)
Automatically selects up to the specified number of concepts via an LLM call.
Parameters:
max_concepts(int): The maximum number of concepts for the system to select out of the set of generated concepts. All of these concepts will be scored when the user calls thescore()function.
Example:
await self.select_auto(max_concepts=8)show_selected
show_selected()
Prints out a summary of the concepts that have been currently selected. The user can make changes via the select() widget and re-run this function to check the current state.
Example:
l.show_selected()score
score(c_ids=None, batch_size=1, get_highlights=True, ignore_existing=True)
Score all documents with respect to each concept to indicate the extent to which the document matches the concept inclusion criteria. Returns a dataframe with the score results.
Parameters:
c_ids(List[str], optional, default: None): A list of IDs (UUID strings) for the concepts that should be scored.batch_size(int, optional, default: 1): Number of documents to score at once in each LLM call. By default, LLooM scores each (concept, document) combination individually to improve scoring reliability. Increasing this number will batch together multiple documents to be scored at once for a given concept.get_highlights(bool, optional, default: True): Whether to retrieve highlighted quotes indicating where the document illustrates the concept.ignore_existing(bool, optional, default: True): Whether to ignore concepts that have previously been scored.
Returns:
score_df(pd.DataFrame): Dataframe summarizing scoring results. Contains the following columns:- doc_id: Unique document ID
- text: Text of the document
- concept_id: Unique ID for the concept (assigned internally)
- concept_name: Name of the concept
- concept_prompt: Prompt conveying the concept inclusion criteria
- score: Concept score (range: [0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0], where 0 indicates no concept match and 1 indicates the highest concept match)
- rationale: LLM-provided rationale for the score
- highlight: LLM-extracted quote from the document that illustrates the concept (if applicable)
- concept_seed: The seed used to generate the concept (if provided)
Example:
score_df = await l.score()get_score_df
get_score_df()
Retrieves the score_df for the current set of active concepts.
Returns:
score_df(pd.DataFrame): Dataframe summarizing scoring results. Refer toscorefor details.
Example:
score_df = l.get_score_df()summary
summary(verbose=True)
Displays a cumulative summary of the (1) Total time, (2) Total cost, and (3) Tokens for the entire LLooM instance.
- Total time: Displays the total time required for each operator. Each tuple contains the operator name and the timestamp at which the operation completed.
- Total cost: Displays the calculated cost incurred by each operator (in US Dollars).
- Tokens: Displays the overall number of tokens used (total, in, and out)
Parameters:
verbose(bool, optional, default: True): Whether to print out verbose output (per-operator breakdowns of time and cost).
Example:
l.summary()Sample output:
Total time: 25.31 sec (0.42 min)
('distill_filter', '2024-03-08-02-45-20'): 3.13 sec
('distill_summarize', '2024-03-08-02-45-21'): 1.80 sec
('cluster', '2024-03-08-02-45-25'): 4.00 sec
('synthesize', '2024-03-08-02-45-42'): 16.38 sec
Total cost: $0.14
('distill_filter', '2024-03-08-02-45-20'): $0.02
('distill_summarize', '2024-03-08-02-45-21'): $0.02
('synthesize', '2024-03-08-02-45-42'): $0.10
Tokens: total=67045, in=55565, out=11480vis
vis(cols_to_show=[], slice_col=None, max_slice_bins=5, slice_bounds=None, show_highlights=True, norm_by=None, export_df=False, include_outliers=False)
Visualizes the concept results in the main LLooM Workbench view. An interactive widget will appear when you run this function.
Parameters:
cols_to_show(List[str], optional, default: []): Additional column names to show in the tablesslice_col(str, optional, default: None): Name of a column with which to slice the data. This should be a pre-existing metadata column in the dataframe. Numeric or string columns are supported. Currently, numeric columns are automatically binned into quantiles, and string columns are treated as categorical variables.max_slice_bins(int, optional, default: 5): For numeric columns, the maximum number of bins to createslice_bounds(List[float], optional, default: None): For numeric columns, manual bin boundaries to use. Example:[0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0]show_highlights(bool, optional, default: True): Whether to show text highlights in the table.norm_by(str, optional, default: None): How to normalize scores for the matrix visualization. Options:"concept"or"slice". If not provided, the scores will not be normalized and the matrix will reflect absolute counts.export_df(bool, optional, default: False): Whether to return a dataframe for export. This dataframe contains the following columns:- concept: Concept name
- criteria: Concept inclusion criteria
- summary: Written summary of the documents that matched the concept
- rep_examples: Representative text examples of the concept
- prevalence: Proportion of total documents that matched this concept
- n_matches: Absolute number of documents that matched this concept
- highlights: Sample of highlighted text from documents that matched the concept
include_outliers(bool, optional, default: False): Whether to include outliers in the export_df (if requested).
Examples:
l.vis()
# With slice column
l.vis(slice_col="n_likes")
# With normalization by concept
l.vis(slice_col="n_likes", norm_by="concept")
# With normalization by slice
l.vis(slice_col="n_likes", norm_by="slice")Check out Using the LLooM Workbench for a more detailed guide on the visualization components. 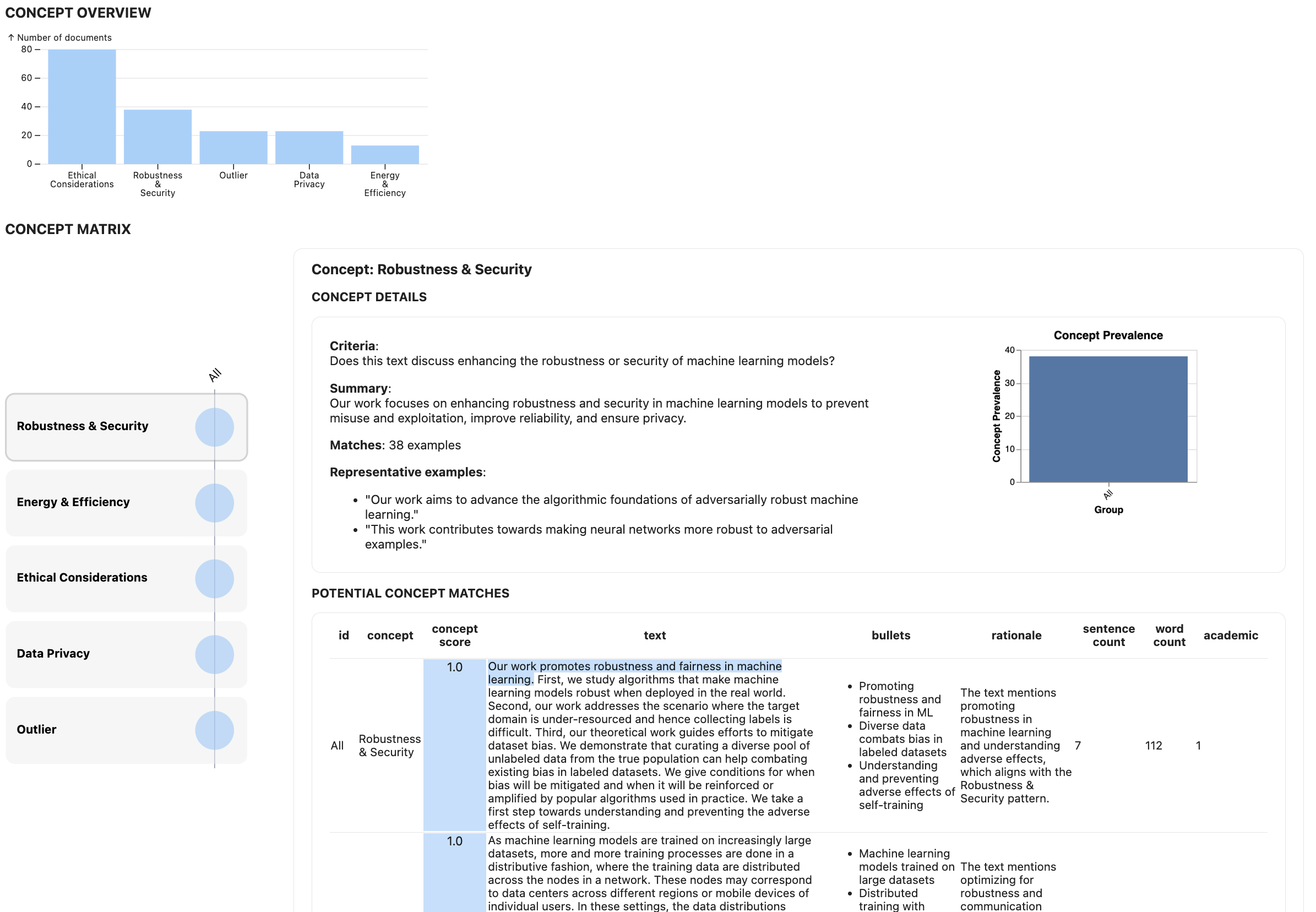
add
add(name, prompt, ex_ids=[], get_highlights=True)
Adds a new custom concepts by providing a name and prompt. This function will automatically score the data by that concept.
Parameters:
name(str): The new concept nameprompt(str): The new concept prompt, which conveys its inclusion criteria.ex_ids(List[str], optional, default: []): IDs of the documents that exemplify this concept.get_highlights(bool, optional, default: True): Whether to retrieve highlighted quotes indicating where the document illustrates the concept.
Example:
await l.add(
# Your new concept name
name="Government Critique",
# Your new concept prompt
prompt="Does this text criticize government actions or policies?",
)save
save(folder, file_name=None)
Save the LLooM instance to a pickle file to reload at a later point.
Parameters:
folder(str): File path of the folder in which to store the pickle file.file_name(str, optional, default: None): Name of the pickle file. If not specified, the system will generate a name based on the current local time.
Example:
l.save(folder="your/path/here", file_name="your_file_name")
# Reloading later
import pickle
with open("your/path/here/your_file_name.pkl", "rb") as f:
l = pickle.load(f)export_df
export_df(include_outliers=False)
Export a summary of the results in Pandas Dataframe form.
Parameters:
include_outliers(bool, optional, default: False): Whether to include the category of outliers (documents that did not match any concepts) in the table.
Returns:
export_df(pd.DataFrame): Dataframe summarizing the concepts. Contains the following columns:- concept: Concept name
- criteria: Concept inclusion criteria
- summary: Written summary of the documents that matched the concept
- rep_examples: Representative text examples of the concept
- prevalence: Proportion of total documents that matched this concept
- n_matches: Absolute number of documents that matched this concept
- highlights: Sample of highlighted text from documents that matched the concept
Example:
export_df = l.export_df()submit
submit()
Allows users to submit their LLooM instance to share their work, which may be selected to be featured in a gallery of results.
Example:
l.submit()You will be prompted to provide a few more details:
- Email address: Please provide an email address so that we can contact you if your work is selected.
- Analysis goal: Share as much detail as you'd like about your analysis: What data were you using? What questions were you trying to answer? What did you find?
estimate_gen_cost
estimate_gen_cost(params=None, verbose=False)
Estimates the cost of running gen() with the given parameters. The function is automatically run within calls to gen() for the user to review before proceeding with concept generation.
Parameters:
params(Dict, optional, default: None): The specific parameters to use within the Distill, Cluster, and Synthesize operators (seegenfor details). If no parameters are provided, the function uses auto-suggested parameters.verbose(bool, optional, default: False): Whether to print a full per-operator cost breakdown
Example:
l.estimate_gen_cost()estimate_score_cost
estimate_score_cost(n_concepts=None, verbose=False)
Estimates the cost of running score() on the provided number of concepts. The function is automatically run within calls to score() for the user to review before proceeding with concept scoring.
Parameters:
n_concepts(int, optional, default: None): Number of concepts to score. If not specified, the function uses the current number of active (selected) concepts.verbose(bool, optional, default: False): Whether to print a full per-operator cost breakdown
Example:
l.estimate_score_cost()auto_suggest_parameters
auto_suggest_parameters(sample_size=None, target_n_concepts=20)
Suggests concept generation parameters based on heuristics related to the number and length of documents in the dataset. Called automatically in gen() and estimate_gen_cost() if no parameters are provided.
Parameters:
sample_size(int, optional, default: None): Number of documents to sample fromdfto determine the parameters. If not provided, all documents will be used.target_n_concepts(int, optional, default: 20): The estimated total number of concepts that the user would like to generate.
Returns:
params(Dict): The parameters to use within the Distill, Cluster, and Synthesize operators. Refer togenfor details.
Example:
params = l.auto_suggest_parameters()